1. 문제
https://school.programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/72413#
프로그래머스
코드 중심의 개발자 채용. 스택 기반의 포지션 매칭. 프로그래머스의 개발자 맞춤형 프로필을 등록하고, 나와 기술 궁합이 잘 맞는 기업들을 매칭 받으세요.
programmers.co.kr
2. 풀이 과정
- 중간 지점을 W라고 하면 S=>W, W=>A, W=>B로 구간을 나눠서 생각한다.
- 각 구간 별 최단 거리 구하기 문제
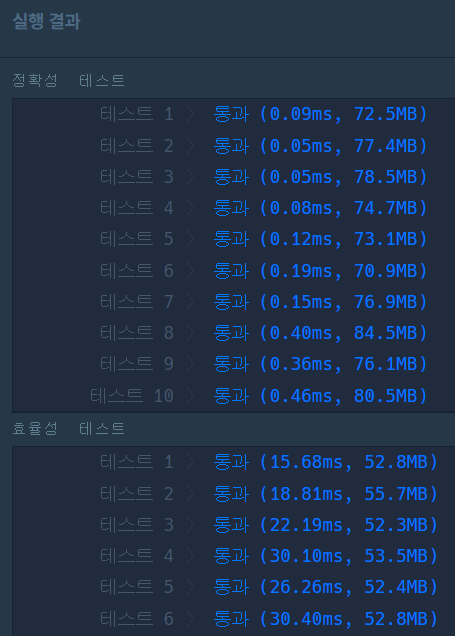
방법1. 플로이드 워샬
- 모든 노드에서 모든 노드까지 전체 최단 거리를 구한다.
- S=>W, W=>A, W=>B까지 모두 더한 값이 최소인 값을 찾는다.
(중복이 있든 말든 상관없지만, 최단거리의 결과는 아마 중복 없게 나올듯 => 왔던 길 다시가는 것보다 한 번씩 가는게 빠를 거니까)
import java.util.*;
//s=>w + w=>A + w=>B
class Solution {
public int solution(int n, int s, int a, int b, int[][] fares) {
int matrix[][] = new int[n+1][n+1];
//초기화 : matrix
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
Arrays.fill(matrix[i], 30_000_000);
matrix[i][i] = 0;
}
for(int i=0; i<fares.length; i++){
int n1 = fares[i][0], n2 = fares[i][1], cost = fares[i][2];
matrix[n1][n2] = cost;
matrix[n2][n1] = cost;
}
//플로이드 => 전체 최소 거리
for(int w=1; w<=n; w++){
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
for(int j=1; j<=n; j++){
matrix[i][j] = Math.min(matrix[i][j], matrix[i][w] + matrix[w][j]);
}
}
}
int answer = matrix[s][a] + matrix[s][b];
for(int w=1; w<=n; w++){
answer = Math.min(answer, matrix[s][w]+matrix[w][a]+matrix[w][b]);
}
//결과
return answer;
}
}
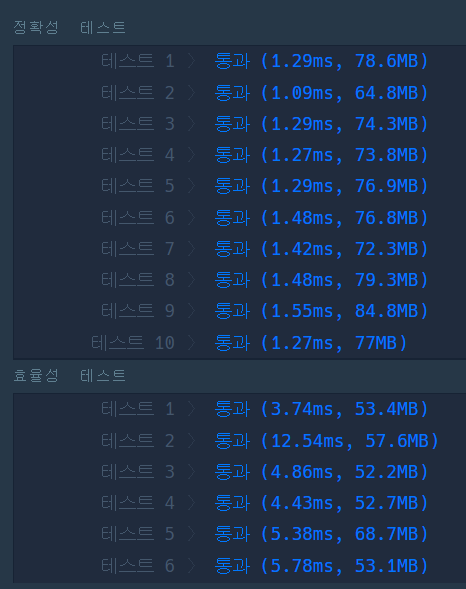
방법2. 다익스트라
- S, A, B를 출발점으로 하여 모든 노드까지의 최단 거리를 구한다.
- 플로이드 워샬과 다르게 시작점이 3개로 축소되었다고 볼 수 있다. 따라서, 아래 방식이 더 빠르다.
import java.util.*;
//s=>w + w=>A + w=>B
class Solution {
public LinkedList<int[]> list[];
public void dijkstra(int start, int[] distance){
//setting
PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2)->o1[1]-o2[1]);
Arrays.fill(distance, 20_000_000);
pq.offer(new int[]{start, 0});
distance[start] = 0;
//
while(!pq.isEmpty()){
int[] now = pq.poll();
if(distance[now[0]]<now[1]){continue;}
for(int[] next : list[now[0]]){
if(distance[now[0]]+next[1] < distance[next[0]]){
distance[next[0]] = distance[now[0]] + next[1];
pq.offer(new int[]{next[0], distance[next[0]]});
}
}
}
}
public int solution(int n, int s, int a, int b, int[][] fares) {
list = new LinkedList[n+1];
//초기화 : 인접리스트
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
list[i] = new LinkedList<>();
}
for(int i=0; i<fares.length; i++){
int n1 = fares[i][0], n2 = fares[i][1], cost = fares[i][2];
list[n1].add(new int[]{n2, cost});
list[n2].add(new int[]{n1, cost});
}
//다익스트라
int start[] = new int[n+1];//S에서 최단거리
int A[] = new int[n+1];//A에서 최단거리
int B[] = new int[n+1];//B에서 최단거리
dijkstra(s, start);
dijkstra(a, A);
dijkstra(b, B);
//결과
int answer = start[1] + A[1] + B[1];
for(int i=2; i<=n; i++){
answer = Math.min(answer, start[i] + A[i] + B[i]);
}
return answer;
}
}
'코딩문제풀이 > 프로그래머스' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Java] 프로그래머스 : 불량 사용자* (0) | 2022.09.29 |
|---|---|
| [Java] 프로그래머스 : 주차 요금 계산 (0) | 2022.09.27 |
| [Java] 프로그래머스 : 등산코스 정하기 (0) | 2022.09.17 |
| [Java] 프로그래머스 : 추석 트래픽 (0) | 2022.09.01 |
| [Java] 프로그래머스 : 피로도 (0) | 2022.09.01 |